FF-PINN 傅里叶特征嵌入
FF-PINN,意思是在输入中添加傅里叶特征(Fourier feature)嵌入,该方法通过使用正弦函数将PINN的输入坐标映射到更高维空间,从而增强了PINN模型的细节表示,从而提高了捕捉精细尺度细节的性能。
具体而言,做了如下变换:
$$
\gamma_{i}(X) = \begin{bmatrix}
\cos(2\pi \beta_{i} X) \
\sin(2\pi \beta_{i} X)
\end{bmatrix}, \quad \text{for } i=1, 2, \ldots, S
$$
这里$\gamma$代表FF,$X$代表PINN的输入向量,参数$\beta$取自高斯分布$N(\mu, \sigma)$。
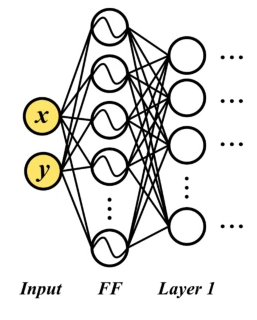
示意图如下,在输入层与第一层隐藏层之间添加了$FF$层:
具体代码实现:
1 | import torch |
这里我们用$3\times2$的输入向量演示:
1 | x = torch.tensor([[1.0,2.0], [2.0,3.0], [3.0,4.0]]) |
1 | tensor([[1., 2.], [2., 3.], [3., 4.]]) |
生成服从正态分布(高斯分布)的随机数
1 | mapping_size = 10 |
1 | tensor([[-1.6859, -1.6255], |
执行Fourier feature mapping函数中的乘法
1 | a = torch.matmul(x, B.t()) |
1 | tensor([[-31.0199, 22.0959, -11.1077, -5.4000, 1.6900, 1.7143, -17.4269, |
返回的$sin$操作,$cos$同理:
1 | print(torch.sin(a2)) |
1 | tensor([[ 0.3857, -0.1046, 0.9937, 0.7728, 0.9929, 0.9897, 0.9890, -0.4391, |
按最后一个维度进行拼接:
1 | a3 = torch.cat([torch.sin(a2), torch.cos(a2)], dim=-1) |
1 | tensor([[ 0.3857, -0.1046, 0.9937, 0.7728, 0.9929, 0.9897, 0.9890, -0.4391, |
这里通过傅里叶特征映射,把torch.Size([3, 2]) 变成了 torch.Size([3, 20]) 。注意mapping_size = 10,因为包含正弦和余弦两个部分,所以输出是 2 * mapping_size 。
具体在PINN中的使用:
1 | # Fourier feature mapping using PyTorch operations |
把FourierFeatures类嵌入神经网络,这里是一个符号距离函数(SDF)网络:
1 | # Define the MLP model with Fourier features |
实例化模型:
1 | neural_SDF = NeuralSDF(B=B) |
参考资料:
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 许可协议。转载请注明来源 一个数字自留地-DIY知识库!




